LIVEP Testing
Home | About | Overview | Lab Testing | Team | Current Studies | Pictures | Media
Flow-Mediated Dilation - Microvascular Function - Pulmonary Function - Exercise Capacity - IMT - Pulse Wave Velocity - Ankle Brachial Index
| Flow-Mediated Dilation |
|
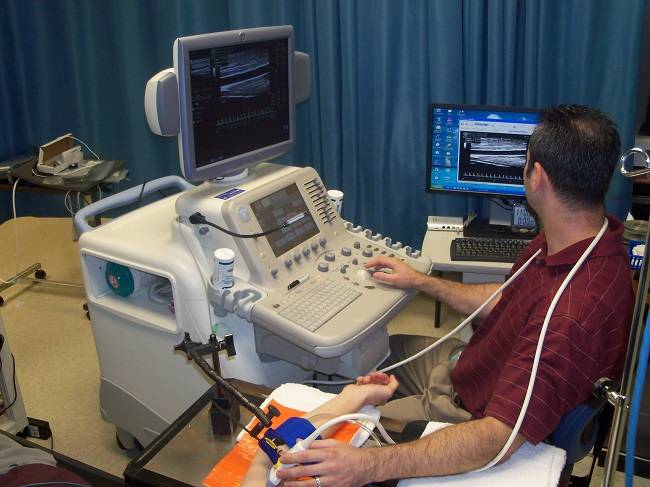
The Flow-mediated dilation (FMD) test is a non-invasive assessment of vascular endothelial function or artery health. Poor artery health is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease risk, the number one cause of death in the United states. Dr. Harris has over 12 years of experience in FMD testing and is recognized as a leader in the field of vascular testing. He wrote the tutorial published in the journal Hypertension for how to perform the FMD test. The total duration of the FMD test is approximately 30 minutes. If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
|
| Maximal Exercise Capacity |
|
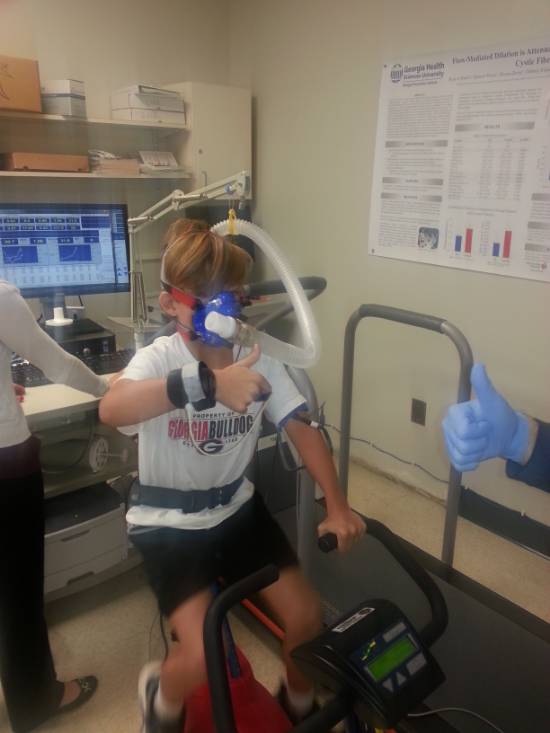
The "gold standard" assessment of exercise capacity is through VO2max testing. There is convincing evidence to indicate an inverse relationship between VO2max and cardiovascular risk, which means that the higher your exercise capacity, the less risk for cardiovascular diseases. During the maximal exercise capacity test, all expired air will be collected through a mouthpiece and analyzed to determine the VO2, or exercise capacity. Heart rate, blood pressure, 12-lead EKG, and rating of perceived exertion (Borg RPE scale 6-20) will be monitored throughout the test in all subjects. Dr Harris is a clinical exercise physiologist and has over 8 years of experience performing maximal exercise tests. The total duration of this test is approximately 45 minutes. If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
 |
| TOP |
| Microvascular Function |
|
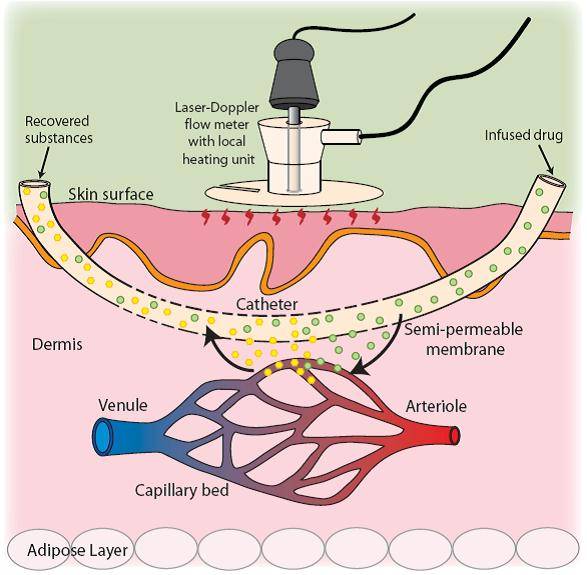
The microcirculation plays a fundamental role in regulating blood flow and blood pressure. In addition to measuring FMD, our lab is equipped to assess cutaneous vascular function, an index of microvascular function. Using Laser Doppler Speckle Imaging (LDSI) and laser doppler flowmetry (LDF) cutaneous vascular flux is determined during reactive hyperemia, heat, and various local drug deliveries during iontophoresis and microdialysis.
|
|
|
Depending on the technique used, the total duration of this test is approximately 30-300 minutes. If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
 |
| TOP |
| Comprehensive Pulmonary Function |
|
Pulmonary Function is a clinical assessment of lung function that is typically performed using spirometry. During different types of breathing maneuvers, measures of lung capacity and expired volumes can be obtained. Although the forced expiratory volume in 1 second and the forced vital capacity have been used to evaluate obstructive and restrictive lung disease, there are other factors that may limit oxygen transport and effect blood flow regulation and oxygen utilization. In addition to assessing spirometry, using the EasyOne Pro Lab, our laboratory conducts a comprehensive assessment of lung function which includes diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO), lung clearance index (LCI), respiratory system impulse oscillometry, and exhaled nitric oxide using the NIOX MINO. The total duration of this comprehensive pulmonary function assessment is approximately 30 minutes. If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu.
|
 |
| TOP |
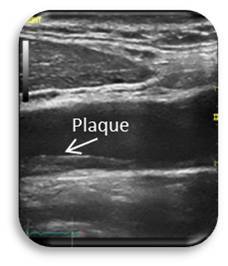
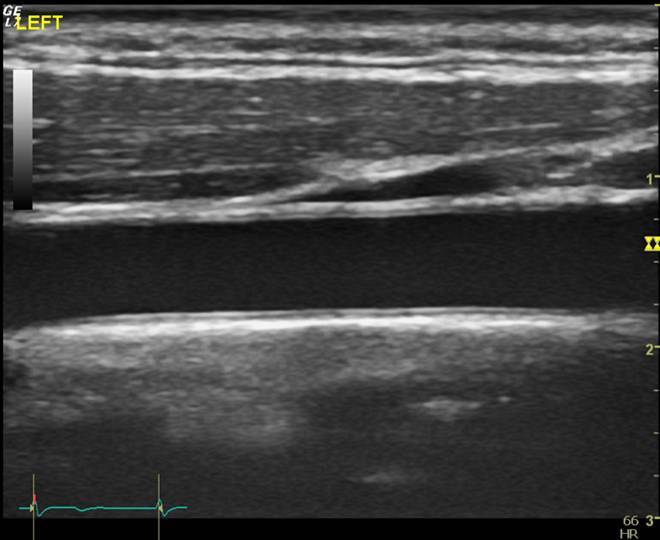
| Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness (cIMT) |
|
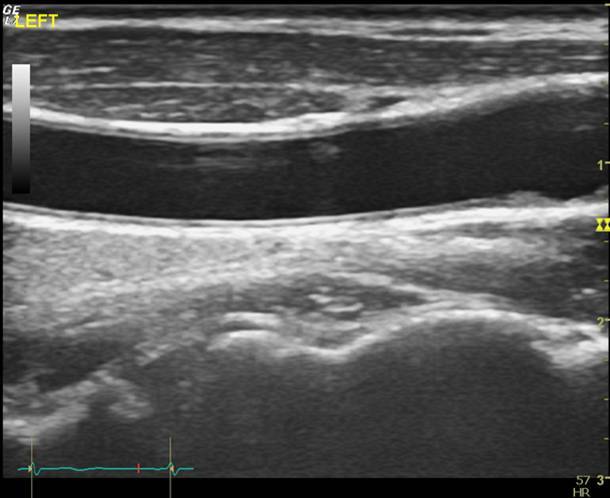
This test measures the thickness of the carotid artery walls, the main artery that feeds the brain. The thickness of the artery in the neck has been used for decades as a clinical tool to measure cardiovascular disease progression and this test can identify local plaque accumulations. The total duration of this test is approximately 20 minutes or shorter if combined with additional vascular testing (i.e. PWV or FMD). If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
|||
|
| TOP |
| Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) |
|
Arterial stiffness is assessed in humans through the measurement of pulse wave velocity (PWV). The PWV measurement is considered the “gold standard” assessment for measuring arterial stiffness non-invasively. PWV is measured by recording high-fidelity pressure waveforms by placing a tonometer on the carotid, radial, and femoral arteries. The time delay between one arterial site and the arrival of the pressure wave at a 2nd site is calculated, and body surface distance between the respective sites are used to calculate PWV (PWV=distance/time). Using the carotid and femoral sites for PWV is considered a valid measurement of aortic stiffness, which has been demonstrated in numerous studies to be a robust independent predictor of cardiovascular disease risk in adults. Carotid-radial (arm) and femoral-dorsalis (leg) PWV are assessments of peripheral artery stiffness and can also be performed, although the clinical significance of these measurements remains unclear. The PWV test is non-invasive, reproducible, and painless. The PWV assessment takes about 30 minutes or shorter if combined with additional vascular testing (i.e. FMD or IMT). If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
| TOP |
| Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) |
|
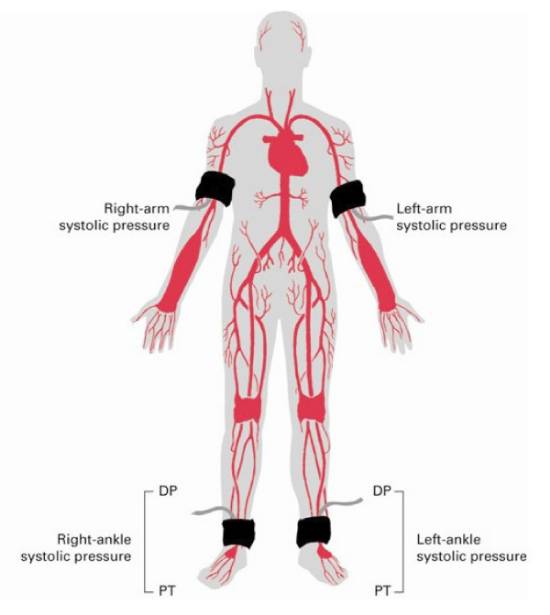
The ABI test measures blood pressure in each limb of the body; right arm, left arm, right leg, and left leg. Blood pressure in the arms is then compared to the blood pressure in the legs to see if there are differences in perfusion between the two limbs. A reduction in perfusion to the legs may be a result of a condition known as peripheral vascular disease or PVD. A normal ABI is 1.0, and ranges anywhere between 0.90 � 1.3. The ABI test is non-invasive and takes about 20 minutes. If you are interested in having this test done or you are interested in collaborating with the LIVEP, contact us at ryharris@augusta.edu. |
 |
| TOP |