- Augusta University
- Centers & Institutes
- Georgia Prevention Institute
- GPI Research
- Bone and Body Composition Laboratory
Bone and Body Composition Laboratory
The GPI Bone and Body Composition Laboratory is a 250 sq. ft room equipped with a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometer (DXA), a peripheral quantitative computed tomographer (pQCT), and a transient elastographer (Fibroscan®).
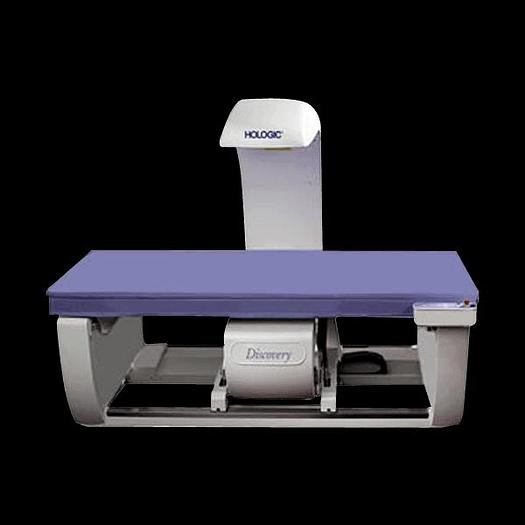
DXA
Model: Hologic Discovery-W (Serial# 84230)
Description: Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) uses small amounts of X-ray radiation at two different energies to provide very accurate assessments of bone health and body composition. Bone health assessments using DXA are considered the 'gold standard' for diagnosing osteoporosis.
Uses: DXA can measure:
- Whole-body, spine, hip, and forearm bone mass and density
- Whole body composition (i.e., fat mass, fat-free soft tissue mass, and body fat percentage)
- Regional body composition (i.e., visceral adipose tissue and subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue)

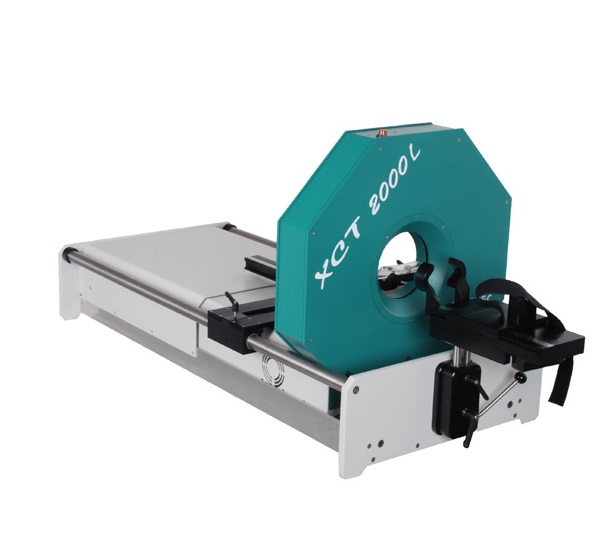
pQCT
Model: Stratex XCT 2000 pQCT (Serial# 2005)
Description: Peripheral quantitative computed tomography (pQCT) uses small amounts of X-ray radiation to take cross-sectional images of the arms and legs. These images are used to assess bone health and muscle size in the extremities. pQCT has advantages over DXA as it: (1) assesses bone in three dimensions allowing for true measures of density; (2) provides accurate measures of bone and muscle size, and; (3) separate bones into different compartments (cortical vs. trabecular).
Uses: pQCT can measure:
- Volumetric bone mineral density
- Bone mineral content
- Bone geometry (area, circumference, thickness)
- Indices of bone strength (section modulus, moment of inertia, strength strain index)
- Muscle cross-sectional area

TRANSIENT ELASTOGRAPHY
Model: Fibroscan® Echosens (Serial# F01033)
Description: Fibroscan® is a non-invasive method for measuring liver stiffness. Vibrations of mild amplitude and low frequency are transmitted from the vibrator to the tissues via the transducer, thereby inducing an elastic shear wave that propagates through the tissue. In the meantime, pulse-echo ultrasound acquisitions allow the propagation of the shear wave to be followed and its velocity to be measured, as these are directly related to tissue stiffness: the stiffer the tissue, the faster the shear wave is propagate.
Uses: Fibroscan® can assess:
- Liver stiffness (kPa)
- Diagnosis of significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in chronic hepatitis C
- Recurrence of hepatitis C after liver transplantation
- Co-infections in HIV-HCV patients and chronic cholestatic diseases