- Augusta University
- Colleges & Schools
- Medical College of Georgia
- Ultrasound Education
- Nephro/Uro Course
Nephro/Uro Course
Renal & Bladder Ultrasound
Renal Ultrasound
The clinical indications for Point of Care Renal Ultrasound are flank pain, abdominal pain, hematuria, urinary hesitancy or incontinence.
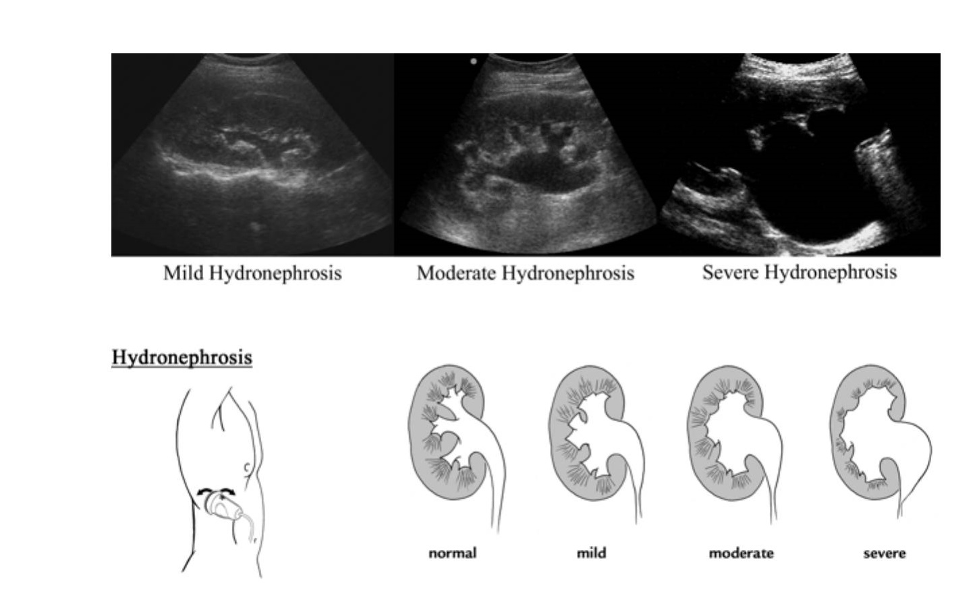
Primary goal of Point of Care Renal Ultrasound is to diagnose hydronephrosis (not to diagnose renal calculi)
Typically ultrasound is not able to detect a ureteral stone but in the appropriate clinical setting with evidence of unilateral hydronephrosis you can suspect a ureteral stone. When there is bilateral hydronephrosis you can suspect a distal obstruction like BPH or abdominal/pelvic cancer/masses causing urinary retention.
Indications for a radiologist ultrasound are renal failure, changes in the bladder wall, changes in kidney size or structure, detection of renal stones, cysts, masses, and vascular studies.
Grades of hydronephrosis
Bladder Ultrasound
Obtain both transverse (cross section with marker to the right) and longitudinal (long axis with marker cephalad) views.
Anatomic Structures
Visualize the hypoechoic (black) bladder with the uterus posterior and superior to the bladder in females and the prostate posterior to the bladder in males.
Post Void Residual Urine Volume: < 20 ml of urine is considered normal in an adult.
Bladder volume measurement can be estimated by H (height) x W (width) x D(depth) x 0.5
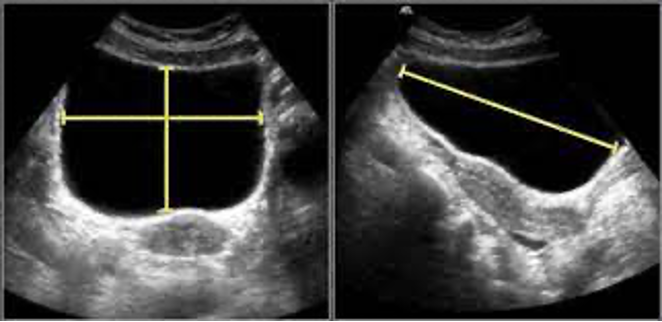
Normal Bladder Measurements
Long axis: 10-12 cm
Short axis: 5 cm
Normal bladder wall thickness
5 mm when empty and
3 mm when full
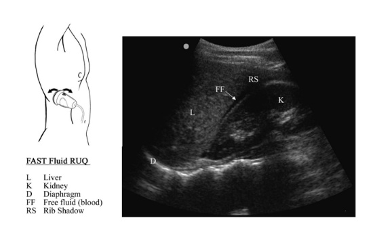
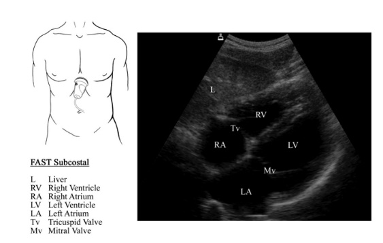
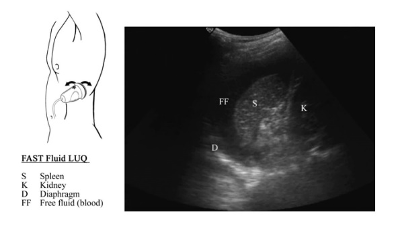
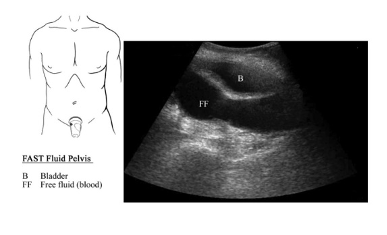
Intro: Focused Assessment in Trauma Exam (FAST)
What is the FAST Exam?
The FAST Exam is an ultrasound protocol to evaluate for free fluid in the abdomen. This exam was originally created for the evaluation of the trauma patient where free fluid in the abdomen would be consistent with blood from internal bleeding. The FAST Exam evaluates 3 compartments for free fluid: 1) around the heart – pericardial effusion, 2) in the thorax – pleural effusion or hemothorax, and 3) in the abdomen – ascites or hemoperitoneum.
At this point you have learned how to obtain all the views required for the FAST exam. We will practice this exam during Urology Lab prior to the Emergency Medicine course so you can master this exam prior to starting clinical rotations.
Please watch the following video link before lab:
How to Perform a FAST Exam