Neurology
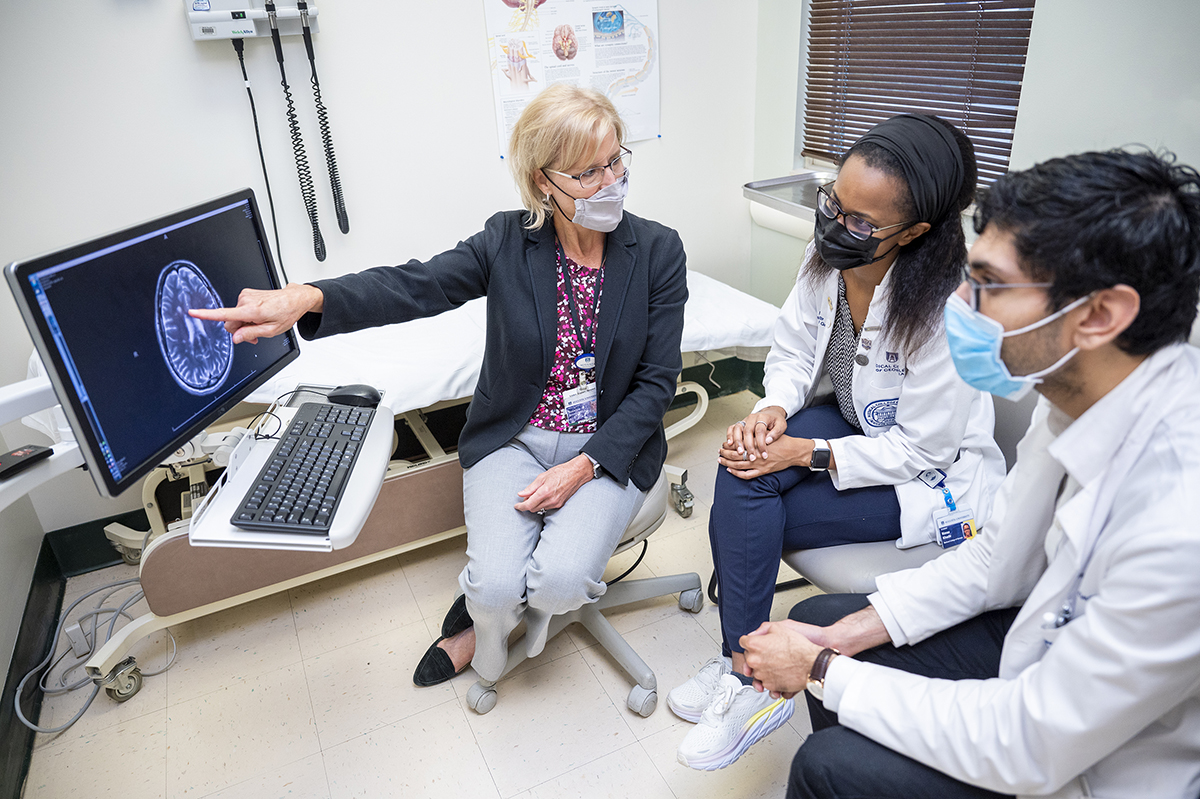
The Department of Neurology at the Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University aims for the highest quality of clinical care, the best training experience for our medical students, residents, and fellows, and the performance of cutting-edge research.
Our teaching mission includes medical students, residents, and fellows undergoing advanced training. Research activities in the department include both basic science and clinical and translational investigations. Additionally, our multidisciplinary Neuroscience Center of Excellence facilitates active collaborations with subspecialists from other departments including general neurosurgery, neuroradiology, neuro-otology, neuro-ophthalmology, functional neurosurgery (deep brain stimulation and epilepsy surgery), neuro-gastroenterology and basic science. Our facility houses a wide variety of other specialties including a level I trauma center, and seven ICUs (neurology, shock trauma, surgery, pediatric, neonatal, cardiology, and medical).
General Neurology & Neurological Subspecialties
Neuroscience Division of Biomedical Visualization
Crafting visuals that are engaging, informative and accessible.
Neurology News

Researchers discover promising CBD-based therapy for fentanyl addiction
Researchers discover promising CBD-based therapy for fentanyl addiction
‘Don't be afraid to take that first step’: Find your pathway in the Bachelor of Social Work program at Augusta University
‘Don't be afraid to take that first step’: Find your pathway in the Bachelor of Social Work program at Augusta University
MCG Center for Healthy Aging, Hess honored with Golden Helix Awards
MCG Center for Healthy Aging, Hess honored with Golden Helix Awards