Chung Sub Kim, PhD
Assistant Professor
 Dept. of Neuroscience & Regenerative Medicine
Dept. of Neuroscience & Regenerative Medicine
Medical College of Georgia
E-mail address: ckim5@augusta.edu
Office phone: (706) 721-7692
Mailing address:
Dept. of Neuroscience & Regenerative Medicine
1120 15th Street, Rm. CA3000
Medical College of Georgia at Augusta University
Augusta, GA 30901
Education:
2006-2011 PhD in Neuroscience, University of Texas at Austin, TX
2001-2003 MS in Medical Science, Yonsei University, South Korea
1996-2001 BS in Microbiology, Inje University, South Korea
Training:
01/2012 - 04/2020 Postdoctoral fellow, Dept. of Neuroscience, Univ. of Texas at Austin, TX
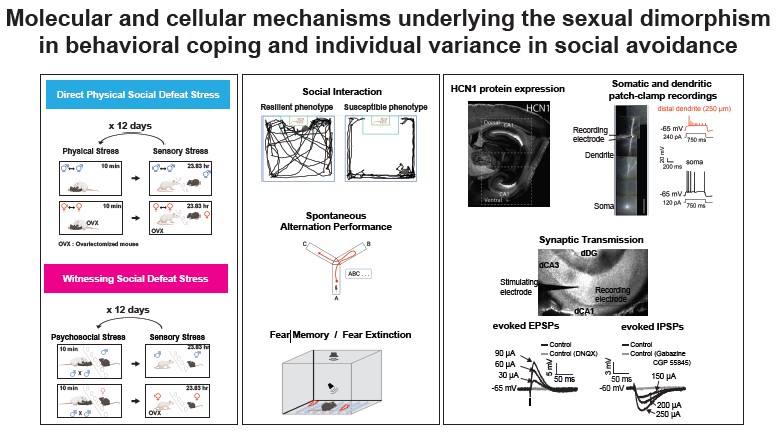
Research Interests:
My research is primarily centered on investigating the cellular and molecular mechanisms that contribute to individual variations and sex differences in social avoidance and stress coping. We employ a comprehensive approach, utilizing a combination of advanced techniques such as electrophysiology—including whole-cell patch-clamp recordings and cell-attached recordings at the soma and dendrites—alongside immunostaining, Western blot, Real-Time PCR, and ELISA. In collaboration with Dr. Kang from the Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, our lab explores in vivo neuronal excitability of hippocampal CA1 neurons using cutting-edge techniques. Dr. Kang's expertise allows us to leverage fiber photometry and head-mounted miniature microscopy.
To model social avoidance, we employ both direct physical and witnessing social defeat stress paradigms. Additionally, we investigate maladaptive fear memory using contextual fear conditioning with post-training of acute stress or corticosterone injection. Our research extends to include the examination of the impact of single-prolonged stress, coupled with post-training corticosterone injection. Through these multifaceted methodologies, we aim to uncover the intricate cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying the observed individual variations and sex differences in social avoidance, stress coping, and maladaptive fear memory.
Selected Publications:
- Kim J, Pokharel K, Sandali M, Kim CS. Establishment of the Mouse Model of Social Avoidance Induced by Female-Directed Female Aggression. Chronic Stress (Thousand Oaks). 2022 Jan-Dec;6:24705470221129288. doi: 10.1177/24705470221129288. eCollection 2022 Jan-Dec. PubMed PMID: 36187211; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC9523834.
- Kim, J., Lei, Y., Lu, XY, and Kim CS. Glucocorticoid-glucocorticoid receptor-HCN1 channels reduce neuronal excitability in dorsal hippocampal CA1 neurons. Molecular Psychiatry (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-022-01682-9
- Fang X, Jiang S, Wang J, Bai Y, Kim CS, Blake D, Weintraub NL, Lei Y, Lu XY. Chronic unpredictable stress induces depression-related behaviors by suppressing AgRP neuron activity. Mol Psychiatry. 2021 Jun;26(6):2299-2315. doi: 10.1038/s41380-020-01004-x. Epub 2021 Jan 11. PubMed PMID: 33432188; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC8272726.
- Kim CS, Johnston D (2020). Antidepressant Effects of (S)-Ketamine through a Reduction of Hyperpolarization-Activated Current Ih. iScience. 23(6):101239. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2020.101239.
- Kim CS, Brager D, and Johnston D (2018). Perisomatic changes in h-channels regulate depressive behaviors following chronic unpredictable stress. Molecular Psychiatry. 23(4):892-903.
- Kim CS, Johnston D (2018). A Possible Link Between HCN Channels and Depression. Chronic Stress. 2:2470547018787781. doi: 10.1177/2470547018787781.
- Kim CS and Johnston D (2015). A1 adenosine receptor-mediated GIRK channels contribute to the resting conductance of CA1 neurons in the dorsal hippocampus.J Neurophysiology. 113(7):2511-23.
- Kim CS, Chang PY, and Johnston D (2012). Knockdown of HCN1 in dorsal hippocampus enhance network activity and leads to anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects. Neuron 9;75(3):503-16