Zheng Dong, PhD

Regents' Professor (part time),
Leon H. Charbonnier Endowed Chair
Department of Cellular Biology and Anatomy
Senior Research Career Scientist, Director of Research Development
Charlie Norwood VA Medical Center
Jump to: Lab Personnel, Education & Post-doctoral Training Honors & Awards Editorship GrantsResearch Interests
Lab Personnel:

Qingqing Wei, PhD, Associate Professor
Man J. Livingston, MD/PhD, Research Scientist
Shixuan Wang, MD/PhD, Assistant Research Scientist
Zhengwei Ma, MD/PhD, Senior Research Associate
Guie Dong, Senior Research Associate
Jialing Yuan, Senior Research Associate
Azeeza Byers, Biomedical PhD Student
Education
1985-1989 B.Sc.
Microbiology, Fudan University, Shanghai, P.R. China
1989-1994 PhD
Physiology, Shanghai Institute of Physiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Post-doctoral Training
1994-1998
University of Texas Health Science Center (UTHSC) at San Antonio
Honors & Awards
| 2000 | Lyndon B. Johnson Research Award | American Heart Association | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2001 | Carl W. Gottschalk Scholar Award | American Society of Nephrology | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2001 | Patricia W. Robinson Young Investigator | National Kidney Foundation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2004 | Career Development Award | VISN 7, Department of Veterans Affairs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | Distinguished Faculty Award (Basic Science) | Medical College of Georgia, MCG | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | Distinguished Research Award | School of Graduate Studies, MCG | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | Research Career Scientist Award | Department of Veterans Affairs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2011 | Regents’ Professorship | University System of Georgia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | Senior Research Career Scientist | Department of Veterans Affairs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2016 | Leon H. Charbonnier Endowed Chair | Augusta University | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2017 | Distinguished Faculty Award in Basic Science | Augusta University | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2020 | Senior Research Career Scientist Award | Department of Veterans Affairs | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- Kidney Diseases (Associate Editor 2019-present)
- Journal of American Society of Nephology (Guest Associate Editor 2014, 2016, 2017,
2021)
Seminar in Nephrology (Guest Editor 2014)
Editorial Board Member
- Kidney International (2010-present)
- Journal of American Society of Nephrology (2015-present)
- American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology (2011-2020)
- American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology (2018-present)
- and others
1) Essentials of Apoptosis: A Guide for Basic and Clinical Research
Editors: Xiao-Ming Yin and Zheng Dong
1st edition, Humana Press, 259 pages.
ISBN: 978-1-59259-361-3, 2003
2nd edition, Humana Press, 707 pages.
ISBN: 978-1-60327-380-0, 2009
http://www.springer.com/us/book/9781603273800
2) Cell Death in Biology and Diseases
Series Editor: Xiao-Ming Yin and Zheng Dong
| NIH | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chartered Member | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2012-2016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ad hoc member: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2006.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2007.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2008.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2010.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2011.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PBKD Study Section 2011.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PCD Study Section 2002.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CSD Study Section 2006.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-G 02, 2009.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-A 58 2009.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-K11 2009.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-G 03, 2009.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-G11, 2010.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-A 05, 2011.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 OBT-Z 50, 2013.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZDK1 GRB-N z(J6), 2013.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Botanical Dietary Supplement Research Centers (P50), 2014.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NCI Special panel ZCA1 RPRB-M (M5) 2016.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NCI Special panel ZCA1 SRB-1 (J1) R 2016.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-J (03) 2016.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-P (91) S 2017.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-P (02) M 2017.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 IDM-C 50 2017.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-P (04) 2017.10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NCI Special panel ZCA1 SRB-A (M1) S 2018.02 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-L (55) 2018.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-G (03) 2020.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZDK1 GRB-M (M1) 2020.04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-P (03) 2020.07 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZRG1 DKUS-W (05) M 2021.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Special panel ZDK1 GRB-S (J1) 1 2023.08 |
Grant Reviewer Continued
| VA: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Career Development Award Program 2006.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2010.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2010.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2011.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2011.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2012.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2019.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RDS/Promotions Review Committee 2019.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2019.12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2020.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| RCS Review Committee 2021.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2021.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ShEEP Review Panel 2023.01 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Merit Review Panel for Nephrology 2023.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASN: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Regular/Chartered member: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ASN Grants Review Committee 2022 - 2023 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DoD: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Army Research Program 2004.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EPSCoR IDeA Program 2006.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PRCRP 2011 D-Kidney Cancer panel 2011.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nebraska Research Initiative 2011.12, 2012.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| University of Toledo Intramural Program 2019.3; 2020.2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio 2019, 2020 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NIDDK Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Program 2021.5 |
International Grant Agencies
| Canada: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) 2020.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| China: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National Basic Research Program 2010.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1000 Talents Program for Young Scholars 2012.11; 2014 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Changjiang Scholar Program 2013.5; 2015.5; 2016.7; 2017.9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding Young Investigator Program 2012; 2015, 2016, 2018 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chinese National Science Foundation 2013-present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| France: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| French National Research Agency 2015.4, 2016.4, 2020.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Germany: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| German Research Foundation 2013.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hong Kong: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research Grant Council (RGC) of Hong Kong Panel Member: 2020-2022 Ad hoc: 2013.3; 2014.3, 2015.3, 2015.8, 2016.3, 2016.9, 2017.3, 2018.3 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Israel: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| US-Israel Binational Science Foundation 2022.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Netherlands: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dutch Cancer Society 2012.7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dutch Kidney Foundation 2018.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Poland: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| National Science Centre 2013.3, 2017.3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romania: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romanian National Council for Scientific Research 2011.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Singapore: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biomedical Research Council Program 2004.2, 2007.5, 2009.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Switzerland: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Swiss National Science Foundation 2016.5, 2021.5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| UK: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cancer Research UK 2011.2, 2018.6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Medical Research Council (MRC) 2011.10, 2021.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Yorkshire Cancer Foundation 2013.8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kidney Research UK 2013.1, 2014.1, 2021.9 |
Research Interests
The long-term goal of our research is to delineate the mechanism of cell death, its protection, and subsequent regeneration during kidney injury and kidney repair. Our current work is focused on mitochondria, metabolism, autophagy, and epigenetic regulation in disease conditions of acute kidney injury and diabetic kidney disease. As of August 1, 2023, we have published 350 full-length articles with a Google Scholar H-index of 94. The publications, including 262 original papers and 88 invited reviews and commentaries, have been cited more than 38,000 times, attesting the contribution to the field of kidney injury and repair in renal diseases and, cell death in general.
Contributions to Science
1. We have delineated the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in hypoxic/ischemic kidney injury, discovered the role of Bak in the regulation of mitochondrial dynamics, and demonstrated the pathogenic role of mitochondrial dynamics disruption in kidney disease. We showed that the mitochondrial pathway is centered on the regulation of outer membrane permeabilization by Bcl-2 family proteins, resulting in the release of apoptogenic factors, such as cytochrome c. Our recent work further demonstrated a striking change of mitochondrial dynamics during cell injury and stress in diseases. We discovered a novel role of Bak in mitochondrial fragmentation and damage under cell stress and disease conditions. We further unveiled Bif-1 as a key regulator of mitochondrial inner membrane dynamics. These studies have been published in >40 research articles and have been cited for >5000 times. We have also contributed authoritative reviews in this field (eg. Zhan M. et. al. Kidney Int 2013; Linkermann et al. JASN 2014; Tang et al. Nature Rev Nephrol 2020). Representative original publications:
Representative Original Publications:
a. Brooks C, Wei Q, Feng L, Dong G, Tao Y, Mei L, Xie Z, Dong Z. Bak regulates mitochondrial morphology and pathology during apoptosis by interacting with Mitofusins. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences (USA) 104: 11649-11654, 2007. PMCID: PMC1913853 (Highlighted by Faculty 1000; with news report) 104: 11649-11654, 2007. PMCID: PMC1913853 (Highlighted by Faculty 1000; with news report).
b. Brooks C, Wei Q, Cho S, Dong Z. Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics in acute kidney injury in cell culture and rodent models. Journal of Clinical Investigation 119: 1275-85, 2009. PMCID: PMC2673870 (with news report).
c. Wei Q, Dong G, Chen J, Ramesh G, Dong Z. Role of Bax and Bak in ischemic acute kidney injury shown by global and proximal tubule-specific knockout mouse models. Kidney International 84:138-48, 2013. PMCID: PMC3686831.
d. Cho S, Xiao X, Wang , Gao H, Rafikov R, Black S, Huang S, Ding HF, Yoon Y, Kirken RA, Yin XM, Wang H-G, Dong Z. Bif-1 interacts with prohibitin-2 to regulate mitochondrial inner membrane during cell stress and apoptosis. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 30:1174-1191, 2019. PMCID: PMC6622411 (Highlighted on Journal cover).
2. We have unveiled a rapid DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and have further determined its pathogenic role. These findings have been verified by other investigators, leading to the recognition of the DNA damage response mediated by ATR/Chk2/p53 as an important pathogenic mechanism in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. The studies have been published in >35 research articles and have been cited for ~3000 times. We have also contributed authoritative reviews in this field (eg. Pabla N et al. Kidney Int 2008; Jiang M et al. JPET 2008; Yang Y et al. Arch Toxicol 2014; Zhu S et al. Arch Toxicol 2015; Tang C et al. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2019).
Representative Original Publications:
a. Jiang M, Wei Q, Wang J, Du Q, Yu J, Zhang L, Dong Z. Regulation of PUMA-alpha by p53 in cisplatin-induced renal cell apoptosis. Oncogene 25:4056-66, 2006. 25:4056-66, 2006.
b.Pabla N, Huang S, Mi QS, Daniel R, Dong Z. ATR-Chk2 signaling in p53 activation and DNA damage response during cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283: 6572 – 6583, 2008. PMID: 18162465 (Highlighted by Faculty 1000).
c. Pabla N, Ma Z, McIlhatton MA, Fishel R, Dong Z. hMSH2 recruits ATR to DNA damage sites for activation during DNA damage-induced apoptosis. Journal of Biological Chemistry 286:10411-8. 2011. PMCID: 3060494.
d. Zhang D, Liu Y, Wei Q, Huo Y, Liu K, Liu F, Dong Z. Tubular p53 regulates multiple genes to mediate acute kidney injury. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 25(10):2278-89, 2014 (Highlighted on journal cover).
3. We have demonstrated the first evidence of autophagy in acute kidney injury and have further established its role in kidney injury and repair. This line of work has been extended by other investigators to show the role and regulation of autophagy in other renal diseases, suggesting a therapeutic approach for kidney protection. The studies have been published in >30 research articles and have been cited for ~3000 times. , We have also contributed authoritative reviews in this field (Periyasamy-Thandavan Set. al. AJP-Renal 2009; Huber et al. Autophagy 2012; Livingston et al. Seminar in Nephrol 2014; Tang et al. Nature Rev Nephrol. 2020).
Representative Original Publications:
a. Periyasamy-Thandavan S, Jiang M, Wei Q, Smith R, Yin X, Dong Z. Autophagy is cytoprotective during cisplatin injury of renal proximal tubular cells. Kidney International 74, 631–640, 2008. PMID: 18509315. (Highlighted by Editorial: Kidney Int 74, 555-7).
b. Jiang M, Wei Q, Dong G, Komatsu M, Su Y, Dong Z. Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute kidney injury. Kidney International 82: 1271-1283, 2012. (highlighted by Editorial: Kidney Int 82: 1250-3; also by Nature Rev Nephrol).
c. Livingston M, Ding H, Huang S, Hill J, Yin X, Dong Z. Persistent activation of autophagy in kidney tubular cells promotes renal interstitial fibrosis during unilateral ureteral obstruction. Autophagy 12:976-98, 2016.
d. Livingston Mang J, Ganley I, Yin X, Dong Z. Clearance of damaged mitochondria via mitophagy is important to the protective effect of ischemic preconditioning in kidneys. Autophagy 15(12):2142-2162, 2019
e. Livingston MJ, Shu S, Fan Y, Li Z, Jiao Q, Yin XM, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z. Tubular cells produce FGF2 via autophagy after acute kidney injury leading to fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis. Autophagy. 2023; 19: 256-277
4. We have reported the first evidence of microRNA and DNA methylation as epigenetic mechanisms in ischemic and cisplatin nephrotoxic kidney injury. We have subsequently delineated the regulation of several specific microRNAs in kidney injury, protection, and repair. These studies, published in >25 research articles, have gained new insights into the pathogenesis of acute kidney injury and recovery, and have suggested novel therapeutic strategies by targeting epigenetics. We have also contributed several reviews (Bhatt et al. AJP-Renal 2011; Wei Q et al. IUBMB Life 2013; Kidney Int 2015; Guo C et al. Nature Rev Nephrol 2019).
Representative Original Publications:
a. Wei Q, Bhatt K, He H, Mi Q, Haase VH, Dong Z. Targeted deletion of Dicer from proximal tubules protects against ischemic acute kidney injury. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 21: 756-761, 2010. PMCID: PMC2865746. (Highlighted on journal cover).
b. Guo C, Pei L, Xiao X, Wei Q, Chen JK, Ding HF, Huang S, Fan G, Shi H, Dong Z. DNA methylation protects against cisplatin-induced kidney injury by regulating specific genes, including interferon regulatory factor 8. Kidney International 92(5):1194-1205, 2017.
c. Wei Q, Sun H, Liu Y, Liu P, M.J. Livingston, Wang J, Liang M, Huo Y, Nahman S, Mei C, Dong Z. miR-668 is induced via HIF-1 in ischemic acute kidney injury to repress MTP18 for mitochondrial dynamics and cell survival. Journal of Clinical Investigation 128: 5448-5464, 2018 (Highlighted by Editorial: JCI 128:5216-8; with news report).
d. Ma Z,Li L,Livingston MJ,Zhang D,Mi Q, Zhang M, Ding HF, Huo Y, Mei C, Dong Z. p53/microRNA-214/ULK1 axis impairs renal tubular autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation 130(9):5011-5026, 2020 (news report).
5. We have discovered a new alternatively spliced checkpoint kinase-1 (named Chk1-S) as a novel regulator of cell cycle and DNA damage response. We have delineated the differential PKCδ signaling pathways in malignant and normal tissues suggesting an effective approach for kidney protection during cisplatin chemotherapy. We have also discovered the novel interaction between Intu and STAT1 in the regulation of cell death and cilia in kidney injury.
Representative Original Publications:
a. Pabla N, Dong G, Jiang M, Huang S, Kumar MV, Messing R, Dong Z. PKCδ is a novel regulator of cisplatin nephrotoxicity and effective target for renoprotection during cancer therapy. Journal of Clinical Investigation 121: 2709-2722, 2011. PMCID: PMC3223835 (news report).
b. Pabla N, Bhatt K, Dong Z. Chk1-S is a splice variant and endogenous inhibitor of Chk1 that regulates cell cycle and DNA damage checkpoints. Proceedings of National Academy of Sciences (USA) 109: 197-202, 2012. PMCID: PMC3252905 (news report).
c. Wang S, Liu A, Wu G, Ding H, Huang S, Dong Z. The CPLANE protein Intu protects kidneys from ischemia-reperfusion injury by targeting STAT1 for degradation. Nature Communications 2018 Mar 26; 9(1):1234. PMCID: PMC5964315.
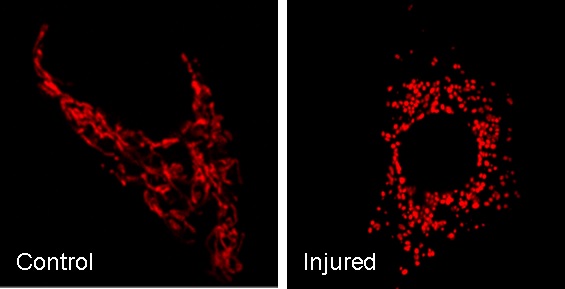
Confocal image of mitochondria. In control cells, mitochondria are elongated and filamentous. After injury, mitochondria are fragmented into short rods or spheres. The morphological change contributes to mitochondrial damage and apoptosis (Brooks…Dong. PNAS 104: 11649-11654, 2007. Journal of Clinical Investigation 119:1275-85, 2009).
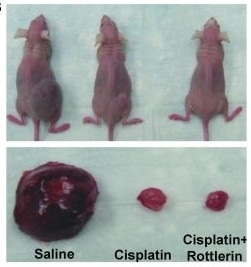 Ovarian cancer xenografts were established in nude mice, which were then treated with
cisplatin with or without Rottlerin, a PKCδ inhibitor. In this and other tumor models,
Rottlerin and relevant protect protect kidneys and enhance cancer therapy effect during
cisplatin treatment. (Pabla…Dong. Journal of Clinical Investigation 121: 2709-2722, 20112011).
Ovarian cancer xenografts were established in nude mice, which were then treated with
cisplatin with or without Rottlerin, a PKCδ inhibitor. In this and other tumor models,
Rottlerin and relevant protect protect kidneys and enhance cancer therapy effect during
cisplatin treatment. (Pabla…Dong. Journal of Clinical Investigation 121: 2709-2722, 20112011).
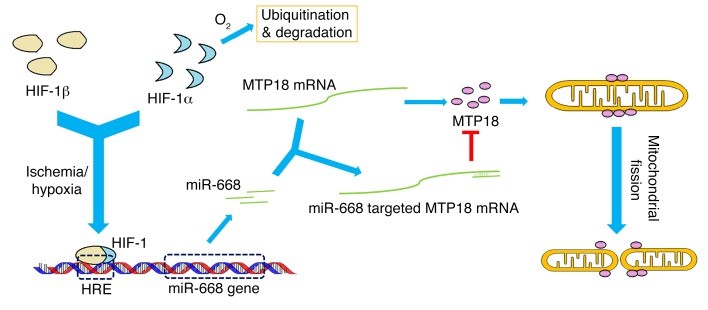
miR-668 is induced via HIF-1 in ischemic acute kidney injury to repress MTP18 for mitochondrial dynamics and cell survival. Wei…Dong. Journal of Clinical Investigation 128: 5448-5464, 2018
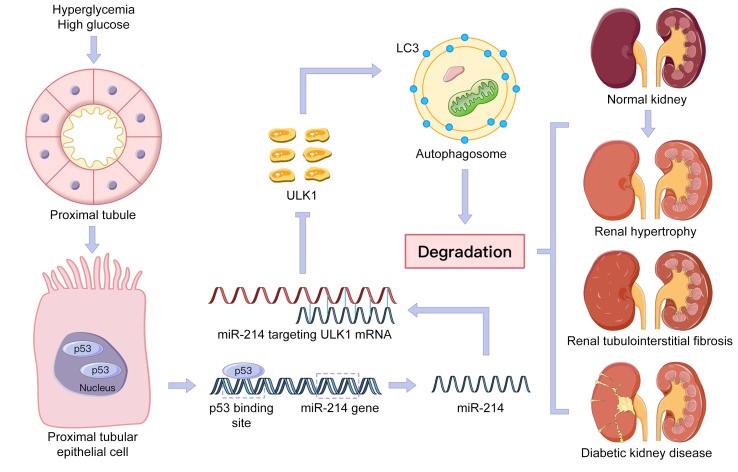
p53/microRNA-214/ULK1 axis impairs renal tubular autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Ma…Dong. Journal of Clinical Investigation 130(9):5011-5026, 2020
Approaches:
Gene cloning, transfection, expression, knockout (antisense and RNAi), promoter assay, genotyping, Northern/Southern blot, microRNA analysis, immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation, immunofluorescence, immunohistochemistry and light/fluorescence/confocal microscopy. In vitro and in vivo experimental models, germline and tissue specific gene knockout mice.
Grant Support:
National Institutes of Health; Department of Veterans Affairs
Representative Publications (2020-2023):
A. Original Studies
1. * Ma Z, Li L, Livingston MJ, Zhang D, Mi Q, Zhang M, Ding HF, Huo Y, Mei C, Dong Z. P53/microRNA-214/ULK1 axis impairs renal tubular autophagy in diabetic kidney disease. Journal of Clinical Investigation 2020;130(9):5011-5026
2. * Cai J, Liu Z, Huang X, Shu S, Hu X, Zheng M, Tang C, Liu Y, Chen G, Sun L, Liu H, Liu F, Cheng J, Dong Z. The deacetylase sirtuin 6 protects against kidney fibrosis by epigenetically blocking β-catenin target gene expression. Kidney Int. 2020 Jan;97:106-118 (with editorial commentary by Gewin L. Kidney International. 2020;97:27-29)
3. * Zhu J, Zhang G, Song Z, Xiang X, Shu S, Liu Z, Yang D, Wei Q, Dong Z. PKCδ mediates kidney tubular injury in renal cold-storage transplantation. Journal of American Society of Nephrology 2020 May;31(5):1050-1065.
4. * Liu Z, Tang C, He L, Yang D, Cai J, Zhu J, Shu S, Liu Y, Yin L, Chen G, Liu Y, Zhang D, Dong Z. The negative feedback loop of NF-kB/miR-376b/NFKBIZ in septic acute kidney injury. JCI Insight 2020 Dec 17;5(24):e142272.
5. * Yan Y, Ma Z, Zhu J, Zeng M, Liu H, Dong Z. miR-214 represses Mitofusin-2 to promote renal tubular apoptosis in ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):F878-F887.
6. * Liu Y, Fu Y, Liu Z, Shu S, Wang Y, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. Irisin is induced in renal ischemia-reperfusion to protect against tubular cell injury via suppressing p53. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2020 Jul 1;1866(7):165792.
7. * Song Z, Zhu J, Wei Q, Dong G, Dong Z. Canagliflozin reduces cisplatin uptake and activates Akt to protect against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Apr 1;318(4):F1041-F1052.
8. * Wang Y, Zhu J, Liu Z, Shu S, Fu Y, Liu Y, Cai J, Tang C, Liu Y, Yin X, Dong Z. The PINK1/PARK2/optineurin pathway of mitophagy is activated for protection in septic acute kidney injury. Redox Biology. 2020 Oct 23;38:101767.
9. * Zhu J, Zeng C, Zhang L, Shu S, Liu Y, Chen G, Liu H, Liu Y, Dong Z. Red Blood Cell Distribution Width and Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio in Predicting Adverse Outcomes of Acute Kidney Injury in Hospitalized Patients. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2020 Sep;6(5):371-381.
10. * Wen J, Ma Z, Livingston MJ, Zhang W, Yuan Y, Guo C, Liu Y, Fu P, Dong Z. Decreased secretion and profibrotic activity of tubular exosomes in diabetic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2020 Oct 1;319(4):F664-F673.
11. * Li F, Sun A, Cheng G, Liu D, Xiao J, Zhao Z, Dong Z. Compound C Protects Against Cisplatin-Induced Nephrotoxicity Through Pleiotropic Effects. Front Physiol. 2020, 23;11:614244.
12. * Liu Z, Yang D, Gao J, Xiang X, Hu X, Li S, Wu W, Cai J, Tang C, Zhang D, Dong Z. Discovery and validation of miR-452 as an effective biomarker for acute kidney injury in sepsis. Theranostics. 2020 Oct 25;10(26):11963-11975.
13. * Yin L, Li H, Liu Z, Wu W, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. PARK7 Protects Against Chronic Kidney Injury and Renal Fibrosis by Inducing SOD2 to Reduce Oxidative Stress. Front Immunol. 2021;12:690697. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.690697.
14. * Wu W, Fu Y, Liu Z, Shu S, Wang Y, Tang C, Cai J, Dong Z.NAM protects against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury by suppressing the PARP1/p53 pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2021 May 1;418:115492.
15. * Wang S, Zhuang S, Dong Z. IFT88 deficiency in proximal tubular cells exaggerates cisplatin-induced injury by suppressing autophagy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;321:F269-F277.
16. * Zeng M, Wen J, Ma Z, Xiao L, Liu Y, Kwon S, Liu Y, Dong Z. FOXO1-mediated Downregulation of RAB27B Leads to Decreased Exosome Secretion in Diabetic Kidneys. Diabetes. 2021;70:1536-1548.
17. * Shu S, Wang H, Zhu J, Liu Z, Yang D, Wu W, Cai J, Chen A, Tang C, Dong Z. Reciprocal regulation between ER stress and autophagy in renal tubular fibrosis and apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 29;12(11):1016.
18. * Fu S, Hu X, Ma Z, Wei Q, Xiang X, Li S, Wen L, Liang Y, Dong Z.p53 in Proximal Tubules Mediates Chronic Kidney Problems after Cisplatin Treatment. Cells. 2022 Feb 17;11(4):712.
19. * Xiang X, Dong G, Zhu J, Zhang G, Dong Z.Inhibition of HDAC3 protects against kidney cold storage/transplantation injury and allograft dysfunction. Clin Science (Lond). 2022;136(1):45-60.
20. * Ma Z, Hu X, Ding H, Zhang M, Dong Z. Single-nucleus transcriptional profiling of chronic kidney disease after cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Am J Pathology 2022;192:613-628.
21. * Cai J, Wang T, Zhou Y, Tang C, Liu Y, Dong Z. Phosphorylation by GSK-3β increases the stability of SIRT6 to alleviate TGF-β-induced fibrotic response in renal tubular cells. Life Sci. 2022 Nov 1;308:120914. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120914.
22. * Fu Y, Wang Y, Liu Y, Tang C, Cai J, Chen G, Dong Z. p53/sirtuin 1/NF-κB Signaling Axis in Chronic Inflammation and Maladaptive Kidney Repair After Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 7;13:925738.
23. * Fu Y, Xiang Y, Wu W, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. Persistent Activation of Autophagy After Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity Promotes Renal Fibrosis and Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 30;13:918732.
24. * Shu S, Wang H, Zhu J, Fu Y, Cai J, Chen A, Tang C, Dong Z. Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to cisplatin-induced chronic kidney disease via the PERK-PKCδ pathway. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jul 27;79(8):452
25. * Mei S, Li L, Zhou X, Xue C, Livingston MJ, Wei Q, Dai B, Mao Z, Mei C, Dong Z. Susceptibility of renal fibrosis in diabetes: Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1. FASEB J. 2022 Aug;36(8):e22477.
26. * Cai J, Wang T, Zhou Y, Tang C, Liu Y, Dong Z.Phosphorylation by GSK-3β increases the stability of SIRT6 to alleviate TGF-β-induced fibrotic response in renal tubular cells. Life Sci. 2022 Nov 1;308:120914.
27. * Li H, Liu Z, Wang Y, Wang H, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z.PARK7 is induced to protect against endotoxic acute kidney injury by suppressing NF-κB. Clin Sci (Lond). 2022 Dec 22;136(24):1877-1891.
28. * Livingston MJ, Shu S, Fan Y, Li Z, Jiao Q, Yin XM, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z. Tubular cells produce FGF2 via autophagy after acute kidney injury leading to fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis. Autophagy. 2023 Jan;19(1):256-277.
29. * Fu Y, Xiang Y, Wang Y, Liu Z, Yang D, Zha J, Tang C, Cai J, Chen G, Dong Z. The STAT1/HMGB1/NF-κB pathway in chronic inflammation and kidney injury after cisplatin exposure. Theranostics. 2023 May 8;13(9):2757-2773.
30. * Wen L, Wei Q, Livingston M, Dong G, Li S, Hu X, Li Y, Huo Y, Dong Z. PFKFB3 mediates tubular cell death in cisplatin nephrotoxicity by activating CDK4. Translation Research. 2023 Mar;253:31-40.
31. * Wang S, Liu A, Su Y, Dong Z. Deficiency of the Planar Cell Polarity Protein Intu Delays Kidney Repair and Suppresses Renal Fibrosis after Acute Kidney Injury. Am J Pathol. 2023; 193(3):275-285
32. * Hu X, Ma Z, Li S, Wen L, Huo Y, Wu G, Manicassamy S, Dong Z. Fibroblast Growth Factor 2 Is Produced By Renal Tubular Cells to Act as a Paracrine Factor in Maladaptive Kidney Repair After Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity. Laboratory Investigation2023 March; 103(3):100009
33. * Li S, Livingston MJ, Ma Z, Hu X, Wen L, Ding HF, Zhou D, Dong Z. Tubular cell senescence promotes maladaptive kidney repair and chronic kidney disease after cisplatin nephrotoxicity. JCI Insight. 2023 Mar 14:e166643.
34. * Zhu J, Xiang X, Hu X, Li C, Song Z, Dong Z. miR-147 Represses NDUFA4, Inducing Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Tubular Damage in Cold Storage Kidney Transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Aug 1;34(8):1381-1397.
B. Invited Reviews/ Commentaries
1. * Wang Y, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. Mitophagy in Acute Kidney Injury and Kidney Repair. Cells. 2020 Feb 1;9(2). pii: E338. doi: 10.3390/cells9020338.
2. * Edelstein C, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z. Autophagy inhibition by chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine could adversely affect acute kidney injury and other organ injury in critically ill patients with COVID-19. Kidney International. 2020; 98: 234–235.
3. * Tang C, Livingston M, Liu Z, Dong Z. Autophagy in kidney homeostasis and health and disease. Nature Reviews Nephrology 16(9):489-508, 2020
4. * Wang S, Dong Z.Is autophagy the culprit of cystogenesis in polycystic kidney disease? EBioMedicine. 2020; 61:103043.
5. * Wang Y, Liu Z, Shu S, Cai J, Tang C, Dong Z. AMPK/mTOR Signaling in Autophagy Regulation During Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Front Physiol. 2020;11:619730.
6. * Wei Q, Dong Z. The yin and yang of retinoic acid signaling in kidney diseases. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2020;130:5124-5126.
7. * Li S, Wen L, Hu X, Wei Q, Dong Z. HIF in Nephrotoxicity during Cisplatin Chemotherapy: Regulation, Function and Therapeutic Potential. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(2):180.
8. * Tang C, Cai J, Yin X, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA, Dong Z. Mitochondrial quality control in kidney injury and repair. Nature Reviews Nephrology 2021;17:299-318.
9. * Liu Z, Dong Z. A cross talk between HIF and NF-κB in AKI. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2021;321:F255-F256.
10. * Wen L, Li Y, Li S, Hu X, Wei Q, Dong Z.Glucose Metabolism in Acute Kidney Injury and Kidney Repair. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 29;8:744122.
11. * Hu X, Ma Z, Wen L, Li S, Dong Z. Autophagy in Cisplatin Nephrotoxicity during Cancer Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Nov 10;13(22):5618.
12. * Xiang X, Zhu J, Dong G, Dong Z. Epigenetic Regulation in Kidney Transplantation. Front Immunol. 2022 Apr 8;13:861498.
13. * Tang TT, Wang B, Lv LL, Dong Z, Liu BC. Extracellular vesicles for renal therapeutics: State of the art and future perspective. J Control Release. 2022 Sep;349:32-50.
14. * Fu Y, Xiang Y, Li H, Chen A, Dong Z. Inflammation in kidney repair: Mechanism and therapeutic potential. Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Sep;237:108240.
15. * Xiang Y, Fu Y, Wu W, Tang C, Dong Z. Autophagy in acute kidney injury and maladaptive kidney repair. Burns Trauma. 2023 Jan 22;11:tkac059.
16. * Tang C, Livingston JM, Safirstein R, Dong Z. Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: new insights and therapeutic implications. Nature Reviews Nephrology. 2023 Jan;19(1):53-72.
17. * Wen J, Zeng M, Yang Y, Liang Y, Fu P, Dong Z. Exosomes in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Dis (Basel). 2023 Feb 14;9(3):131-142.
18. * Chen G, Dong Z. Targeting a Single Codon to Rescue Septic Acute Kidney Injury. Journal of American Society of Nephrology. 2023 Feb 1;34(2):179-181.
19. * Wang S, Hu J, Dong Z. From Primary Cilia and Planar Cell Polarity to Kidney Injury and Repair. Nephron. 2023 Jul 17:1.
20. * Cai J, Dong Z. Two-way communication between the nucleus and mitochondria via a micropeptide in renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2023 May;103(5):833-835.